MANOTERRA decodes
August 2025

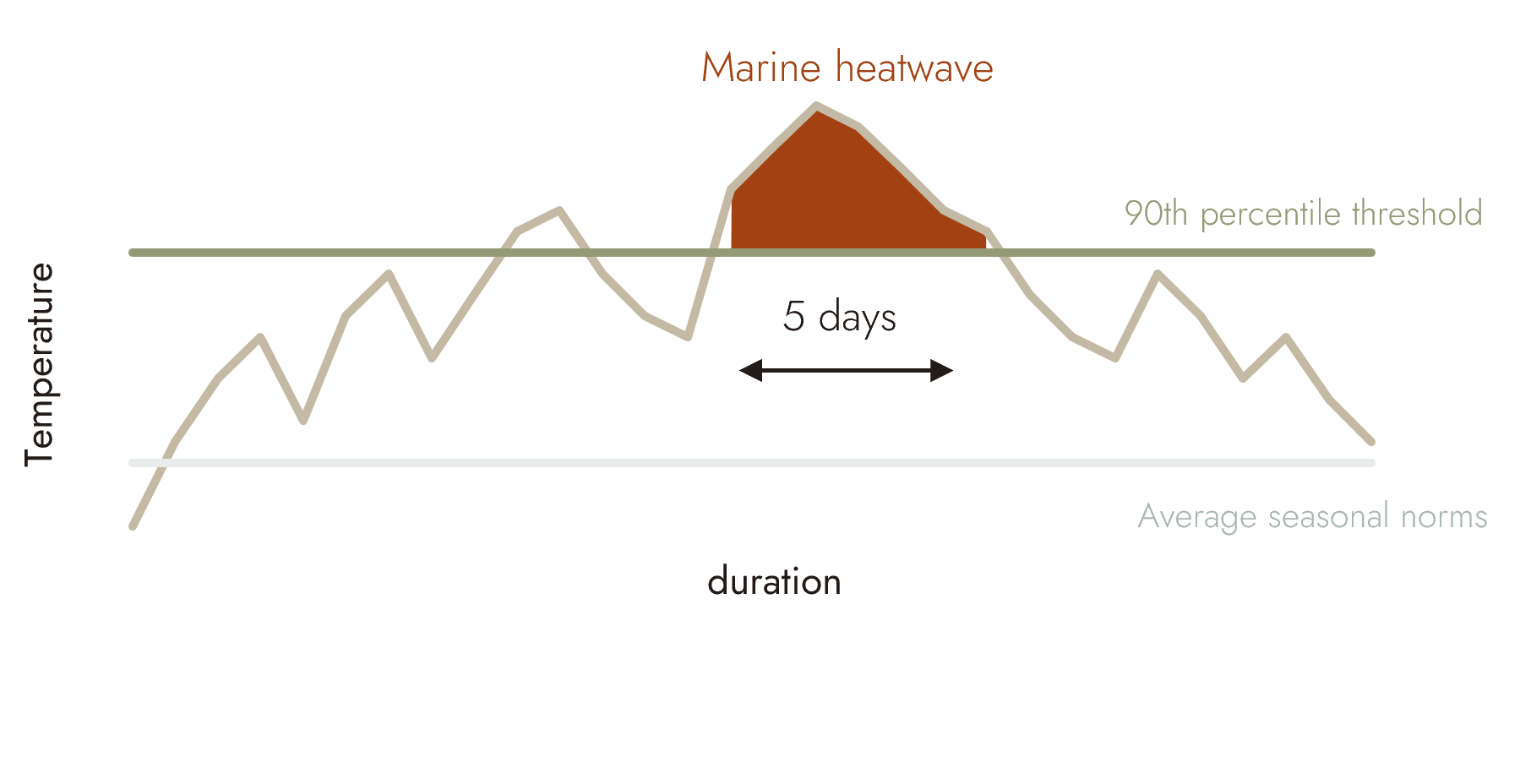
A marine heatwave occurs when the sea surface temperature is above seasonal averages (90th percentile) for more than five consecutive days.
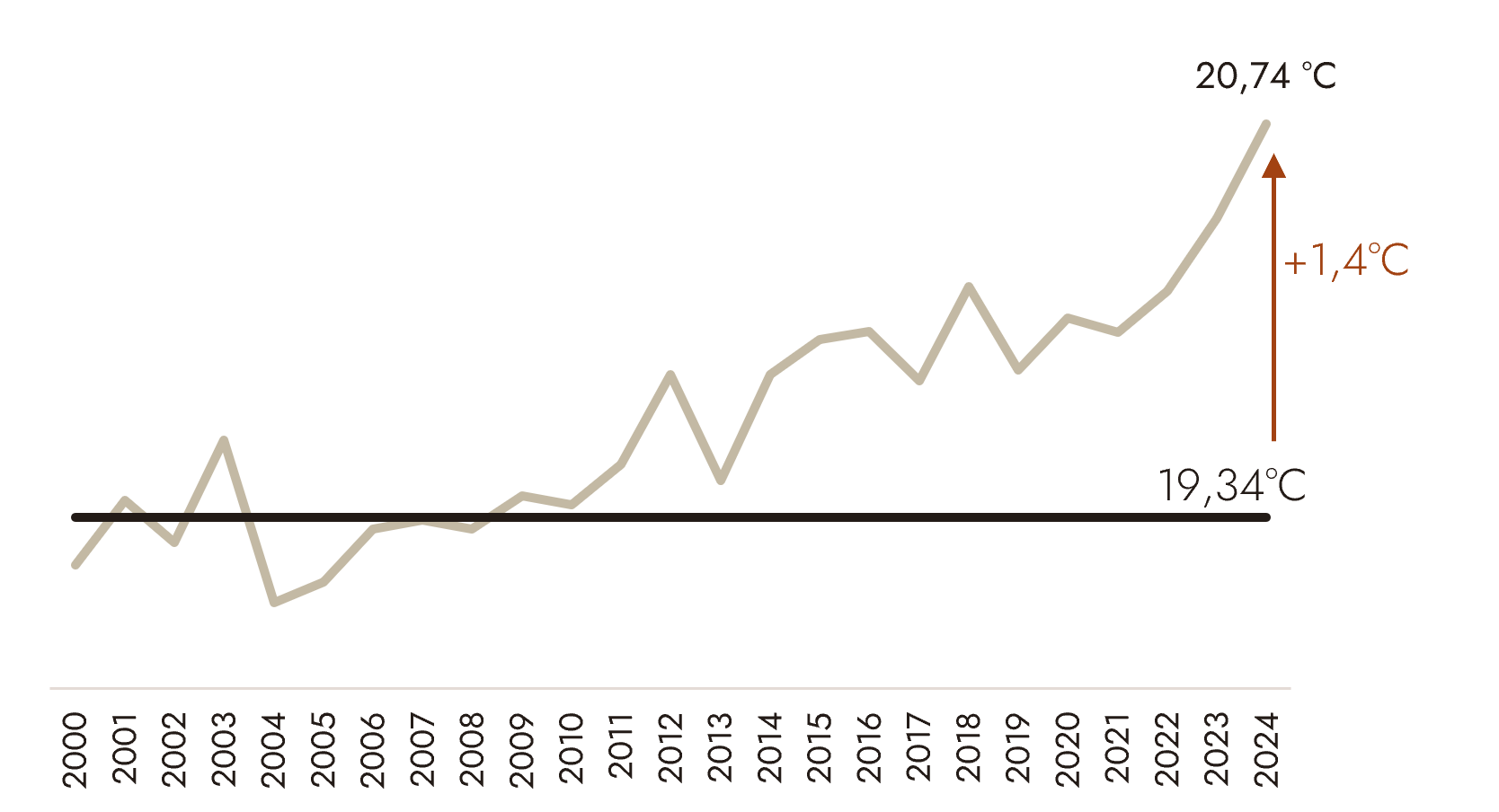
Since the early 2000s, the deviation from the 1991–2020 average has shifted permanently into positive territory and is increasing, with increasingly marked summer peaks. In recent years, the average anomaly has been around +1°C, confirming structural warming in the Mediterranean basin.
Underwater heat waves cause: Mass mortality of immobile ecosystems (corals, seagrass beds, sponges) Significant displacement or loss of mobile biodiversity due to oxygen depletion caused by excessive water temperatures A decrease in carbon sequestration. Organisms such as phytoplankton are no longer able to act as carbon sinks. Risks of methane degassing
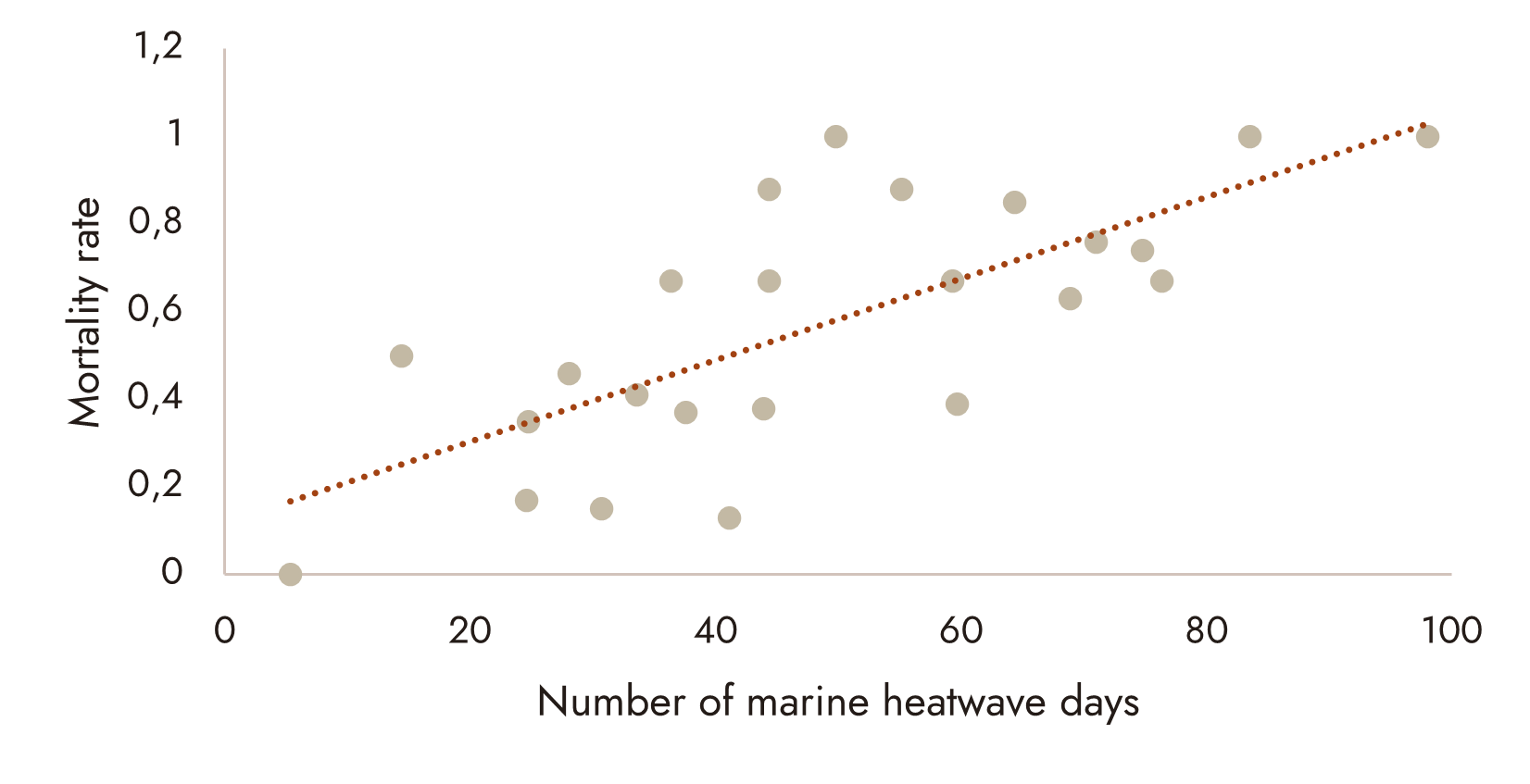
Sources : Marine Heatwave Tracker (NOAA & partenaires), Copernicus Marine – OMI Méditerranée